1. Database selection
RILseqDB currently supports three bacteria: E. coli K-12 MG1655, enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) and Klebsiella pneumoniae str. SGH10. By default, RILseqDB shows data of E. coli K-12 however, this can be changed for the current session by clicking on the bacterium sign () at the top right corner next to the RNA search field, and selecting another database. Once the database was changed, all the interactions and searches will refer to data from the specified bacterium.
2. Search Modes
2.1. RNA
The RNA search is accessible through the top right corner of the navigation bar. This search mode provides an overall view of a particular RNA of interest, including the following details:
- The genomic region where the RNA is encoded.
- Additional features extracted from the RNA interactions that were found to be predictive of sRNAs (Bar et al. 2021).
- A list of the RNA's interacting partners, showing the conditions in which the interaction was found. This table also include links to inspect the interaction.
Tips:
- In case no match was found for a RNA searched by its name, RNAs with most similar names will be suggested.
2.2. Interactions
This type of search can be found under the advanced search menu in the website's navigation bar. The interaction search allows the user to retrieve all interactions between two RNAs (termed first and second interactor) according to either their names or genomic annotations. There are several advantages to this search mode:
- It lists interactions identified in multiple growth conditions.
- It enables to search for interactions by the genomic annotation of RNAs (e.g., CDS, 3'UTR).
- It generates dynamic tables, such that the user can apply further filtering on top of a search.
- The generated tables are exportable.
Tips:
- To select any RNA, leave the name definition filed empty.
2.3. Shared Interactor
The shared interactor search allows the user to retrieve common interactors of a query RNA. This search mode is useful for finding common regulators of target RNAs or for finding common targets of known regulators.
NOTE:
- This search mode does not differentiate between CDS and 5UTR targets. It means that if one interactor interacts with gene_1 and another interactor interacts with gene_1.5UTR but not gene_1 itself, it still returns gene_1 and gene_1.5UTR as common interactors of the query RNA.
3. RIL-seq Annotations
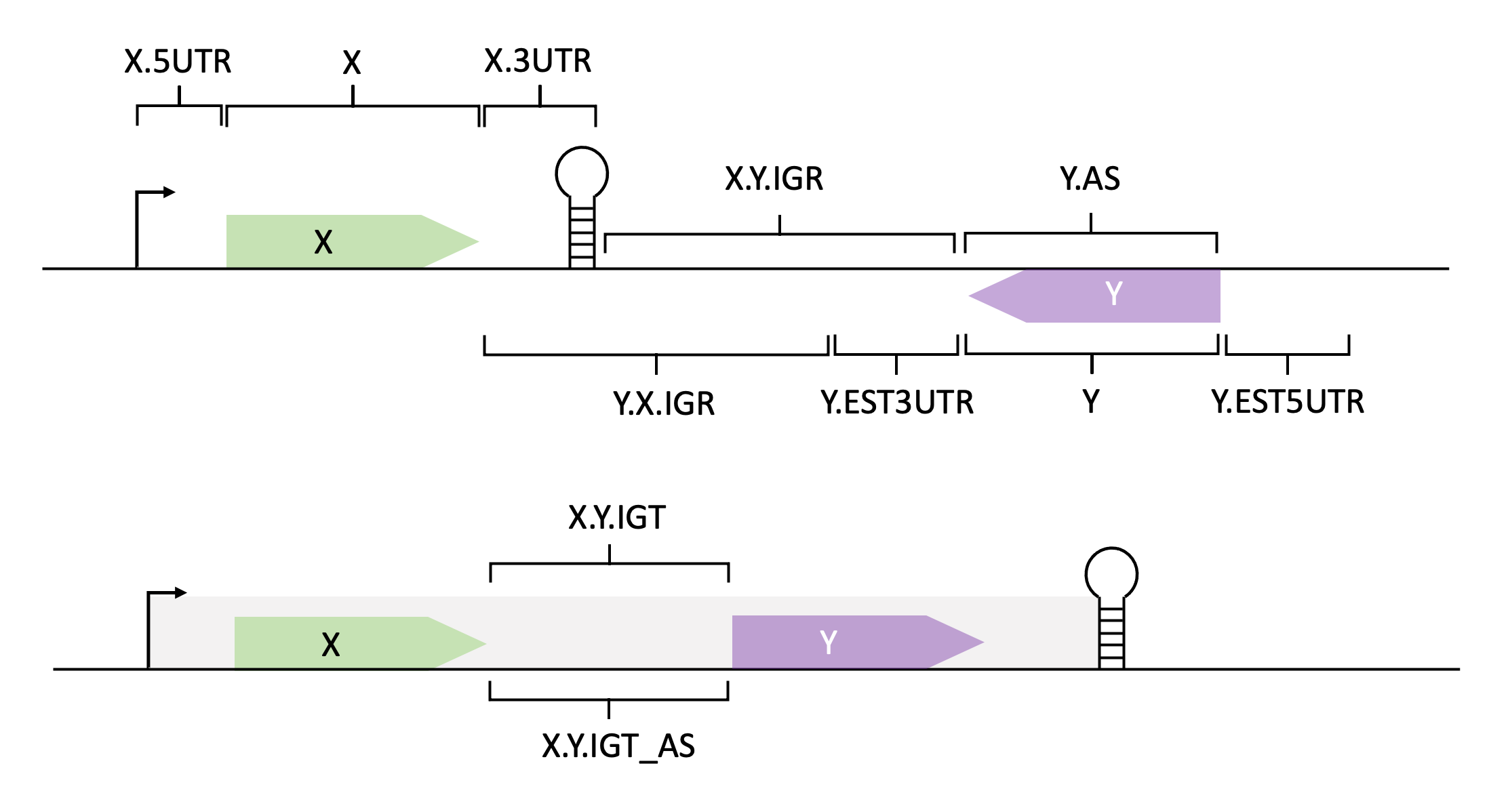
The RIL-seq pipeline generates annotations based on BioCyc-like organism resources. The IDs and names found in these files are used to annotate not only genes, but also the entire genome. Thus, RIL-seq annotation system introduces slight modifications to these IDs and names, which indicate the genomic origin of transcripts. To read more on the annotation process by RIL-seq see Melamed et al., 2016. The IDs and names of the genomic origin are listed below:
- CDS (coding sequence)
- 3UTR (3' UTR) - Trailing '.3UTR' if the region has a known terminator or '.EST3UTR' if it is an estimated 3’UTR (100 nucleotides downstream the stop codon).
- 5UTR (5' UTR) - Trailing '.5UTR' if the region has a known transcription start site or '.EST5UTR' if it is an estimated 5’UTR (100 nucleotides upstream the AUG).
- sRNA
- tRNA
- rRNA
- oRNA (other non-coding RNAs)
- IGR (Intergenic region) - '[name_1].[name_2].IGR' where 'name_1' and 'name_2' are the names of flanking genes.
- IGT (Intergenic within an operon transcript) - '[name_1].[name_2].IGT' where 'name_1' and 'name_2' are the names of the flanking genes transcribed in an operon
- AS (antisense)
- IGT_AS for putative AS RNAs antisense to an IGT.
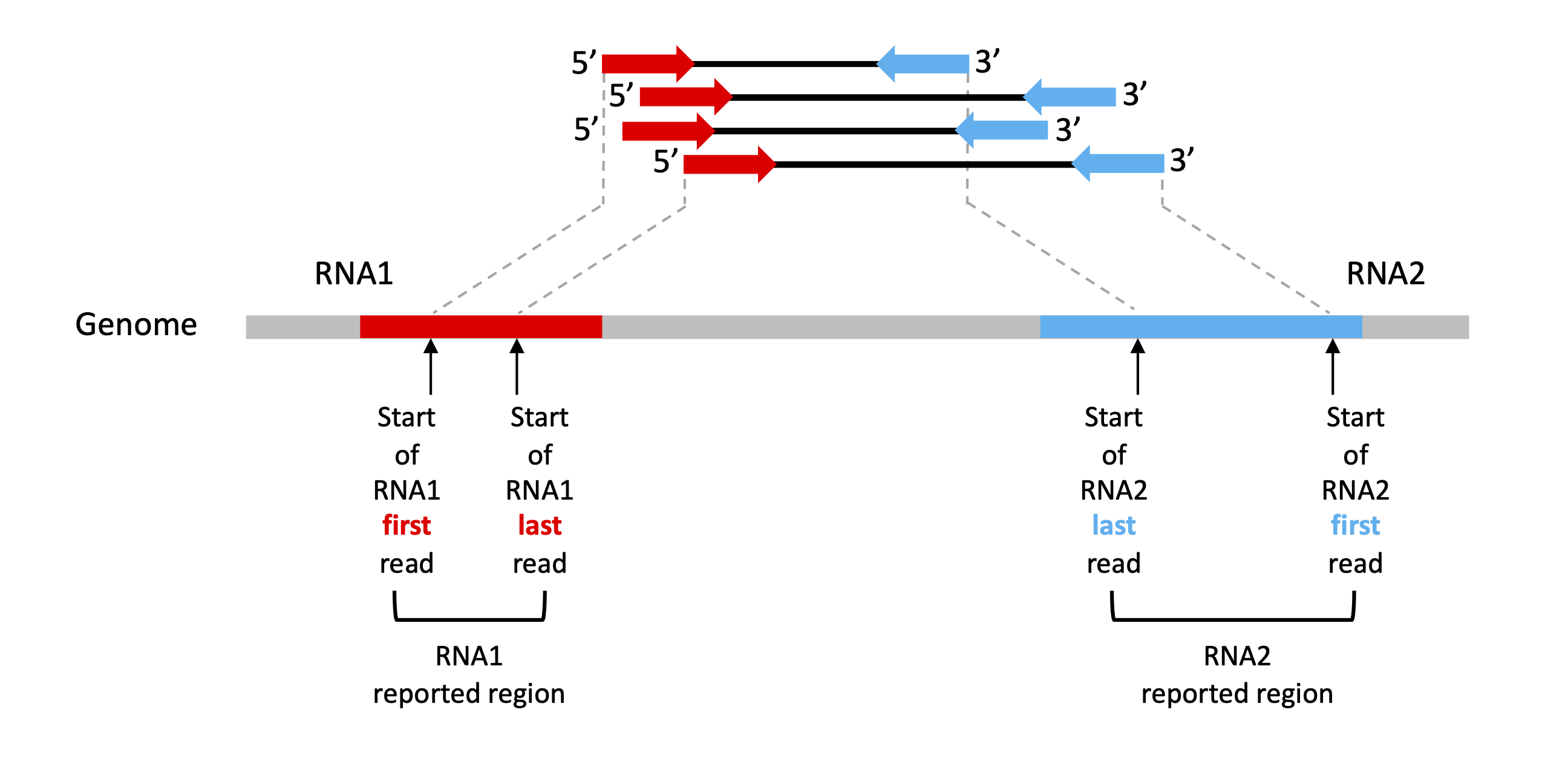
4. RIL-seq Reported Regions
RIL-seq statistically significant interactions are represented by a set of chimeric fragments of two RNAs derived from two genomic regions. The reported chimeric fragment regions represent the starting positions of the chimeric reads (see figure below). In some cases, the reported region may be extremely narrow (even 1 to 2 nucleotide long) if all the reads started almost in the same genomic position. Thus, it is important to keep in mind that the actual reads are longer than the reported region for further analysis.